For The Love Of Tape
The following is to provide you with the basic advantages of tape and things to consider when determining the best adhesive tape for your application and/or certain industries.
- Why we love tape
- The advantages of using tape
- What Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) tape is
- The construction of PSA tape
- Single coated PSA tapes
- Double coated PSA tapes
- Transfer PSA tapes
- Double liner transfer PSA tapes
- Self wound PSA tapes
- Adhesives used with PSA tapes
- The cost and characteristics of tape adhesives
- What to consider for making a PSA tape decision
Why We Love Tape
One of the reasons designers and engineers love adhesive tapes is the sheer versatility of these materials. Adhesive Tape is used in many different applications with new uses being discovered every year. The usage of tape will continue to grow as a solution to fastening and joining due to advances in adhesive technology, ease of use, and its low cost compared to traditional fastening systems.
The Advantages of Using Tape
- Replaces bolts, rivets, welds and other heavy mechanical fasteners.
- Lighter thinner materials.
- Bonds dissimilar materials without incompatibility concerns.
- Acts as a moisture seal/environmental barrier.
- Provides vibration deadening and noise reduction.
- Shortens assembly time.
- Eliminates the need for surface refinishing to remove weld distortions.
- Eliminates visible mechanical fasteners for cosmetic superiority.
- Provides adhesion to difficult surfaces such as glass.
- Provides uniform thickness and gap filling properties.
- Eliminates the need for bonding “both” substrates together at the same time and location providing optimum manufacturing flexibility.
What Pressure Sensitive Adhesive (PSA) Tape Is
Pressure Sensitive Adhesive Tape is a major category of adhesive tapes and is a relatively thin flexible tape with single or double sided coating. When applied to most clean and dry surfaces with pressure, PSA tape will adhere to a variety of substrates. The bond is directly influenced by the amount of pressure which is used to apply the adhesive to the surface. Pressure Sensitive adhesives do not require solvent, water, or heat to activate the adhesive and therefore, used in many different applications with new uses being discovered almost daily.
The Construction Of PSA Tape
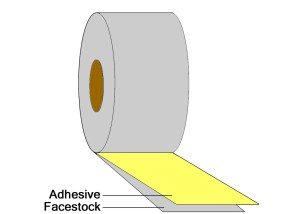
Single Coated PSA Tape:
An adhesive coated on one side of a material (Facestock). The adhesive is protected by a silicone coated release liner.
- Typical uses of single coated tapes include label stock, wound care products, duct and insulation tapes.
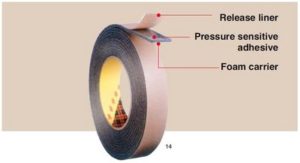
Double Coated PSA Tape & VHB:
A carrier is coated on both sides with PSA. The adhesive carrier can be a wide variety of materials including plastic films, tissue, nonwovens, etc. Typical uses include laminates and carpet tape.
- Typical benefits of using double coated tapes include:
- Carrier offers ease of handling and slitting.
- Can serve to reduce over laminating on porous materials.
- Carrier offers ability to use different adhesives on each side (differential adhesive), enhancing application flexibility.
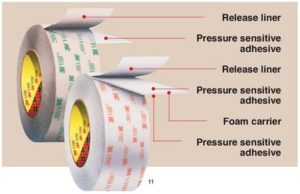
Transfer PSA Tape:
An unsupported mass of adhesive film coated on a release liner which has a release coat on both sides. Transfer tapes offer good conformability to irregular surfaces.
- Typical uses of transfer tape include nameplate application, bonding, foam bonding graphic displays, splicing etc.

Double Liner Transfer PSA Tapes
An unsupported adhesive film protected by a release liner on both sides. Each liner is silicone coated on the side facing the adhesive. Generally used where the adhesive needs to be die cut prior to hand installation of adhesive to a finished part.
- Typical uses of double liner transfer tapes are commonly used in membrane switch industry and decorative overlays.
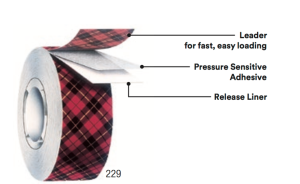
Self Wound:
A carrier which is coated on one side with PSA and on the other with a release coating. There is no release liner with these types of products. Carton sealing, Duct and Masking are all examples of self wound tapes.
- Typical uses for self wound tapes include packaging tapes, electrical tapes, masking tapes, and duct tapes.
Adhesives Used With PSA Tapes
Rubber:
Adhesives which are based on natural or synthetic rubbers and formulated with tackifying resins, oils and anti-oxidants. Rubber is the most cost effective PSA and offers quick stick capability. Rubber adhesive is not recommended for high heat applications.
Acrylic:
Adhesives formulated with acrylic polymers and generally has a better long term aging and more resistance to solvents and environmental factors. Acrylic adhesives typically develop a stronger bond than the traditional Rubber adhesive and are able to take higher temperatures
Silicone:
Formulated with Silicone polymers and the only adhesive that will bond well with silicone substrates. Silicone adhesives are relatively expensive and have a very low initial tack, but can withstand higher temperatures than both Rubber and Acrylic adhesive.
The Cost and Characteristics Of Tape Adhesives
| Characteristic | Rubber | Acrylic | Silicone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lowest | Med/High | Very High |
| Tack | Med/High | Med/Low | Low |
| Temp. Resistance | Low | High | Very High |
| Adhesion | Med/High | Moderate/High | Med/Low |
| Shear | Med/High | Moderate/High | Excellent |
| Solvent Resistance | Poor | Good | Excellent |
| UV Resistance | Poor | Excellent | Excellent |
| Plasticizer Resistance | Poor | Moderate/Good | Excellent |
| Low-surface energy materials | Excellent | Poor/Moderate | Poor |
| High-surface energy materials | Excellent | Excellent | Moderate |
What To Consider Before Making A PSA Tape Decision
Can-Do National tape offers a large selection of Pressure Sensitive Tapes and Representatives to help you choose the best solution. However, below you will find 5 topics you should consider when purchasing an PSA Tape.
- What is the material/substrate the adhesive will be sticking to?
- What are the conditions the tape will be exposed to, Temperature, Moisture, UV, Chemicals?
- What is the function of the PSA?
- How will the PSA be applied?
- Is it a permanent or temporary application?


